Business
Dozens of Texas businesses back challenge to abortion ban: ‘This is why our economy is taking a hit’ on December 14, 2023 at 4:32 pm Business News | The Hill
Ambiguities in Texas’s abortion ban are making it harder for businesses in the state to recruit, a coalition of businesses argued on Thursday.
Fifty-one businesses have signed onto an amicus brief filed by in-house counsel at dating site Bumble, which was filed in support of 22 women suing the state over the abortion ban.
The plaintiffs in that case — Zurawski v. Texas — are 20 former patients who argue that they were denied medically necessary abortions because physicians were afraid of legal consequences.
As a tech company largely run by women, Bumble CEO Whitney Wolfe Herd said she feels it has a duty not just to provide access to health care, “but to speak out – and speak loudly – against the retrogression of women’s rights.”
The businesses signing onto the letter — which include dating sites Bumble and Match (which owns Match.com and Tinder), advertising giants Preacher and GDS&M, event organizers SXSW and the United States Women’s Chamber of Commerce as well as dozens of Texas real estate, law firms and restaurant groups — argued that the state’s abortion laws make it unattractive for families looking to move to a place where they can have children.
In the wake of the Supreme Court decision overturning Roe v. Wade, Texas has enacted a near-total ban on abortion after a fetus has a heartbeat, which typically occurs around 6 weeks into pregnancy and often before a woman knows she is pregnant.
After that point, the state allows the procedure only when it’s deemed medically necessary — an exception that the Zurawski plaintiffs, and others, argue is overly ambiguous and has not translated into legal abortions in the real world.
The uncertainty in those laws “has impacted, and will continue to impact, companies doing business in Texas, companies thinking about doing business in Texas, employees living in or traveling to Texas, and individuals considering relocating to Texas,” the letter reads.
“Because of those undeniable realities, businesses are now forced to confront this issue head on — not for moral or legal reasons — but to keep the lights on and people working, making money,” it continues.
“No sector of the Texas economy is immune.”
The state’s GOP leadership has sought to attract transplants from other states to Texas, which it has cast as a pro-business, small government paradise: a place with no income tax and consistent local regulations and where parents’ rights in schools reign supreme.
But the Bumble letter draws together case studies of prospective transplants — including oil company executives — who decided against moving to Texas based on their desire to start a family.
It also emphasizes the risk felt even by women who are visiting the state on business — or for the lucrative professional conventions that Texas cities compete to attract.
In 2023, for example, the Society of Women Engineers (SWE) — an organization with 40,000 members — announced it would not hold conferences in “any location where there are limits on reproductive” healthcare, a list that incudes Texas.
SWE was joined in this move by other professional societies, like the Society for Integrative and Comparative Biology, and the Journal of Urology, which cited the duty of conference organizers “to reasonably ensure female urologists can safely attend without the threat of catastrophic health consequences.”
The Bumble filing draws on research that found that nearly half of young women in nine battleground states are considering or making plans to move to a state with “comprehensive protections” for reproductive healthcare, and nearly two-thirds of college educated workers nationwide would not consider a job in a state with abortion restrictions.
To make matters worse, women and their doctors don’t have a clear picture of what conditions are exceptional enough to allow them to secure abortions under the exception for medically necessary cases, filing author Sarah Stewart of law firm Reed Smith told The Hill.
“The Zurawski question is: what standard doctors need to meet? Is it good faith medical judgment or something else?” Stewart asked.
Stewart added that the inherent complication and unintended consequences that attend pregnancy make a set-it-and-forget-it list of exceptions untenable. “If it’s an objective standard, then the state will always be able to come up with another doctor who will testify that the abortion wasn’t necessary — so that brings no comfort, and no clarity and certainty to the doctor,” ” she told The Hill.
In essence, Stewart added, the exceptions leave state doctors in the same place as an explicit ban, only now “with the threat of very severe consequences if it turns out that they guessed wrong.”
All this means that the abortion ban is costing the state $15 billion per year in lost revenue as qualified candidates go elsewhere and women of childbearing age stay out of the workforce, according to a 2021 report by the Institute for Women’s Policy Research cited in the Bumble letter.
The businesses that signed on to the Bumble filing argue that these costs are falling on them. To draw people to states where abortion bans are in place, businesses are now having to beef up their medical policies to pay for travel so that employees can get reproductive healthcare outside the state, the letter notes — something that corporations from Microsoft and Disney to Google and Wells Fargo now offer.
Critics of Texas’s abortion laws, passed in 2021 and 2022, have pointed to the disjunction between the start-point of the state’s ban and the timeline when most women learn they’re pregnant as a troubling source of uncertainty.
The Bumble letter — and the broader Zurawski challenge it is a part of — emphasize that the laws’ cut-off point also conflicts with another timeline: the one when some women with badly wanted pregnancies receive the brutal news that their fetuses have serious medical conditions.
The state’s ban kicks in long before parents get such news.
For example, genetic testing — which can reveal lethal fetal abnormalities like trisomy 13, Tay Sachs or anencephaly — can only be performed after about 10 weeks of pregnancy.
That testing is how Kate Cox — the Dallas-area woman at the center of a court battle over the ban who just fled Texas to secure an out-of-state abortion — found out roughly 20 weeks into pregnancy that the fetus she was carrying had trisomy 18, a rare and generally fatal condition that leads to rampant abnormalities throughout the body.
Like many of the Zurawski plaintiffs, Cox was told by her doctors that her health would be at risk if she didn’t get an abortion — but she was unable to obtain the procedure under the state’s ban despite it’s exception for medically necessary cases.
The standard for this exception, Zurawski plaintiffs argue, is dangerously unclear, and the penalties for doctors who get it wrong are very high. Those can include felony charges of up to 99 years in prison, civil fines of up to $100,000 and — even if the state ignores the case — potential lawsuits under Senate Bill 8 from any private citizen who feels the abortion was unnecessary.
That’s a restrictive understanding of the ban — but also one the Texas Supreme Court seemed to affirm in Cox’s case.
The court ruled on Monday evening that protections are available to doctors who perform abortions only if the mother’s life is definitely at risk, and that since Cox’s doctor had not used the phrase “life-threatening physical condition” in the filing that sought to secure her an abortion, she had not met the standard.
Similarly to Cox, Zurawski plaintiff Lauren Hall had to travel to Washington to get an abortion after her fetus was diagnosed with anencephaly — a fatal condition in which a fetus develops without a skull or brain.
In that case, Hall recalled to The Texas Tribune, her doctor advised her to sneak out of state.
The state legislature in 2023 passed some reforms allowing abortion in limited cases. But the court’s Monday ruling on Cox’s case strongly implies that little has changed in the law’s practical application since Hall’s flight.
Cases like those tell women thinking of a move to Texas that the state is “fundamentally unserious” about protecting women and newborns, said Rachel O’Leary Carmona, executive director of Women’s March.
O’Leary Carmona said that dynamic is particularly clear when the abortion ban is stacked up against Texas’s high maternal mortality rate and its lack of mandatory paid maternity leave or state support for recent mothers.
“There’s not any demonstrable policy that deals with the issue of actually giving women the support that they need to have to have a reasonable choice to become a mother,” she added.
The Bumble letter echoed those concerns. As medical practitioners leave Texas to avoid being caught in its abortion ambiguities, it’s creating a feedback loop “that further pushes away business and workers,” Stewart wrote.
Cox’s case, she said, “are why businesses will continue to struggle to recruit and retain talent. This is why pregnant women from other states are hesitant to travel to Texas for business meetings. This is why doctors are leaving the state.”
“This is why our economy is taking a hit.”
Business, Health Care, News, Policy, State Watch Ambiguities in Texas’s abortion ban are making it harder for businesses in the state to recruit, a coalition of businesses argued on Thursday. Fifty-one businesses have signed onto an amicus brief filed by in-house counsel at dating site Bumble, which was filed in support of 22 women suing the state over the abortion ban. The plaintiffs in that…
Business
Google Accused Of Favoring White, Asian Staff As It Reaches $28 Million Deal That Excludes Black Workers

Google has tentatively agreed to a $28 million settlement in a California class‑action lawsuit alleging that white and Asian employees were routinely paid more and placed on faster career tracks than colleagues from other racial and ethnic backgrounds.
- A Santa Clara County Superior Court judge has granted preliminary approval, calling the deal “fair” and noting that it could cover more than 6,600 current and former Google workers employed in the state between 2018 and 2024.

How The Discrimination Claims Emerged
The lawsuit was brought by former Google employee Ana Cantu, who identifies as Mexican and racially Indigenous and worked in people operations and cloud departments for about seven years. Cantu alleges that despite strong performance, she remained stuck at the same level while white and Asian colleagues doing similar work received higher pay, higher “levels,” and more frequent promotions.
Cantu’s complaint claims that Latino, Indigenous, Native American, Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islander, and Alaska Native employees were systematically underpaid compared with white and Asian coworkers performing substantially similar roles. The suit also says employees who raised concerns about pay and leveling saw raises and promotions withheld, reinforcing what plaintiffs describe as a two‑tiered system inside the company.
Why Black Employees Were Left Out
Cantu’s legal team ultimately agreed to narrow the class to employees whose race and ethnicity were “most closely aligned” with hers, a condition that cleared the path to the current settlement.

The judge noted that Black employees were explicitly excluded from the settlement class after negotiations, meaning they will not share in the $28 million payout even though they were named in earlier versions of the case. Separate litigation on behalf of Black Google employees alleging racial bias in pay and promotions remains pending, leaving their claims to be resolved in a different forum.
What The Settlement Provides
Of the $28 million total, about $20.4 million is expected to be distributed to eligible class members after legal fees and penalties are deducted. Eligible workers include those in California who self‑identified as Hispanic, Latinx, Indigenous, Native American, American Indian, Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islander, and/or Alaska Native during the covered period.
Beyond cash payments, Google has also agreed to take steps aimed at addressing the alleged disparities, including reviewing pay and leveling practices for racial and ethnic gaps. The settlement still needs final court approval at a hearing scheduled for later this year, and affected employees will have a chance to opt out or object before any money is distributed.
H2: Google’s Response And The Broader Stakes
A Google spokesperson has said the company disputes the allegations but chose to settle in order to move forward, while reiterating its public commitment to fair pay, hiring, and advancement for all employees. The company has emphasized ongoing internal audits and equity initiatives, though plaintiffs argue those efforts did not prevent or correct the disparities outlined in the lawsuit.
For many observers, the exclusion of Black workers from the settlement highlights the legal and strategic complexities of class‑action discrimination cases, especially in large, diverse workplaces. The outcome of the remaining lawsuit brought on behalf of Black employees, alongside this $28 million deal, will help define how one of the world’s most powerful tech companies is held accountable for alleged racial inequities in pay and promotion.
Business
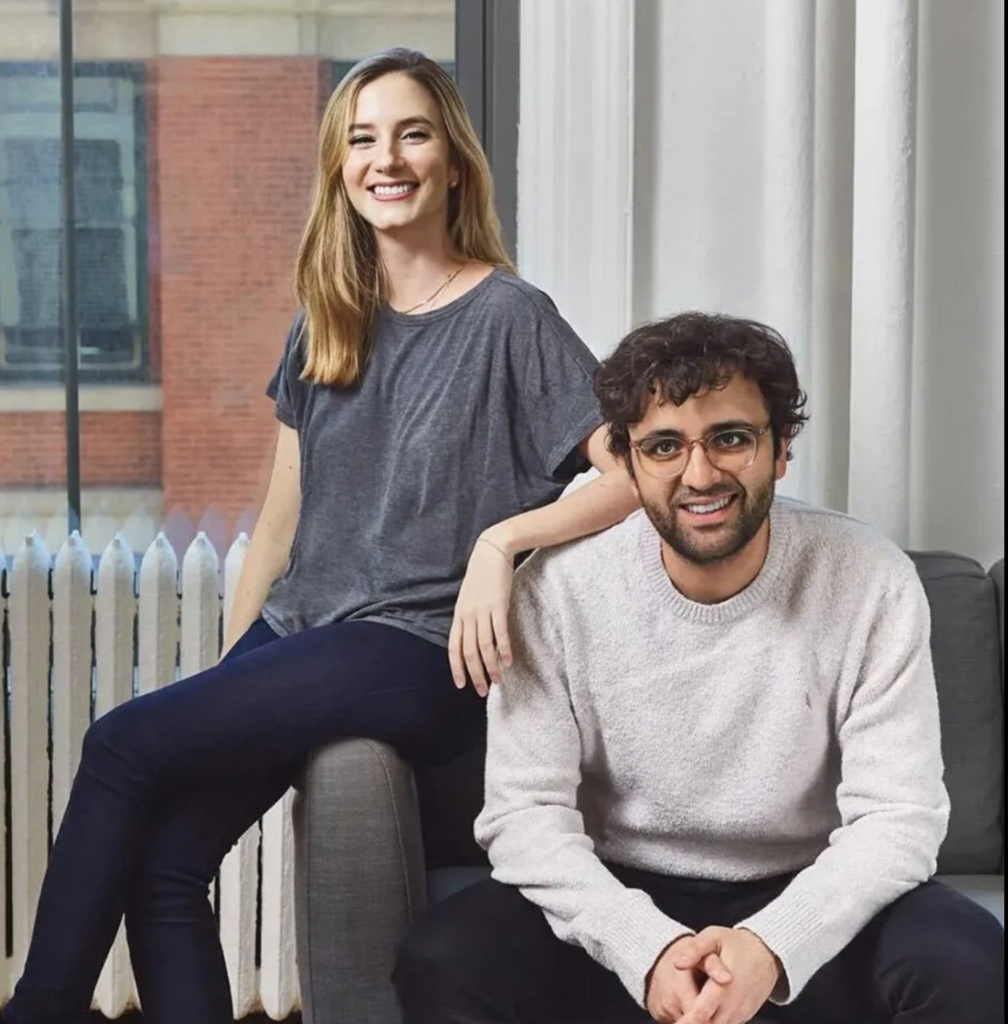
Luana Lopes Lara: How a 29‑Year‑Old Became the Youngest Self‑Made Woman Billionaire

At just 29, Luana Lopes Lara has taken a title that usually belongs to pop stars and consumer‑app founders.
Multiple business outlets now recognize her as the world’s youngest self‑made woman billionaire, after her company Kalshi hit an 11 billion dollar valuation in a new funding round.
That round, a 1 billion dollar Series E led by Paradigm with Sequoia Capital, Andreessen Horowitz, CapitalG and others participating, instantly pushed both co‑founders into the three‑comma club. Estimates place Luana’s personal stake at roughly 12 percent of Kalshi, valuing her net worth at about 1.3 billion dollars—wealth tied directly to equity she helped create rather than inheritance.

Kalshi itself is a big part of why her ascent matters.
Founded in 2019, the New York–based company runs a federally regulated prediction‑market exchange where users trade yes‑or‑no contracts on real‑world events, from inflation reports to elections and sports outcomes.
As of late 2025, the platform has reached around 50 billion dollars in annualized trading volume, a thousand‑fold jump from roughly 300 million the year before, according to figures cited in TechCrunch and other financial press. That hyper‑growth convinced investors that event contracts are more than a niche curiosity, and it is this conviction—expressed in billions of dollars of new capital—that turned Luana’s share of Kalshi into a billion‑dollar fortune almost overnight.
Her path to that point is unusually demanding even by founder standards. Luana grew up in Brazil and trained at the Bolshoi Theater School’s Brazilian campus, where reports say she spent up to 13 hours a day in class and rehearsal, competing for places in a program that accepts fewer than 3 percent of applicants. After a stint dancing professionally in Austria, she pivoted into academics, enrolling at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to study computer science and mathematics and later completing a master’s in engineering.
During summers she interned at major firms including Bridgewater Associates and Citadel, gaining a front‑row view of how global macro traders constantly bet on future events—but without a simple, regulated way for ordinary people to do the same.

That realization shaped Kalshi’s founding thesis and ultimately her billionaire status. Together with co‑founder Tarek Mansour, whom she met at MIT, Luana spent years persuading lawyers and U.S. regulators that a fully legal event‑trading exchange could exist under commodities law. Reports say more than 60 law firms turned them down before one agreed to help, and the company then spent roughly three years in licensing discussions with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission before gaining approval. The payoff is visible in 2025’s numbers: an 11‑billion‑dollar valuation, a 1‑billion‑dollar fresh capital injection, and a founder’s stake that makes Luana Lopes Lara not just a compelling story but a data point in how fast wealth can now be created at the intersection of finance, regulation, and software.
Business
Harvard Grads Jobless? How AI & Ghost Jobs Broke Hiring

America’s job market is facing an unprecedented crisis—and nowhere is this more painfully obvious than at Harvard, the world’s gold standard for elite education. A stunning 25% of Harvard’s MBA class of 2025 remains unemployed months after graduation, the highest rate recorded in university history. The Ivy League dream has become a harsh wakeup call, and it’s sending shockwaves across the professional landscape.

Jobless at the Top: Why Graduates Can’t Find Work
For decades, a Harvard diploma was considered a golden ticket. Now, graduates send out hundreds of résumés, often from their parents’ homes, only to get ghosted or auto-rejected by machines. Only 30% of all 2025 graduates nationally have found full-time work in their field, and nearly half feel unprepared for the workforce. “Go to college, get a good job“—that promise is slipping away, even for the smartest and most driven.
Tech’s Iron Grip: ATS and AI Gatekeepers
Applicant tracking systems (ATS) and AI algorithms have become ruthless gatekeepers. If a résumé doesn’t perfectly match the keywords or formatting demanded by the bots, it never reaches human eyes. The age of human connection is gone—now, you’re just a data point to be sorted and discarded.
AI screening has gone beyond basic qualifications. New tools “read” for inferred personality and tone, rejecting candidates for reasons they never see. Worse, up to half of online job listings may be fake—created simply to collect résumés, pad company metrics, or fulfill compliance without ever intending to fill the role.
The Experience Trap: Entry-Level Jobs Require Years
It’s not just Harvard grads who are hurting. Entry-level roles demand years of experience, unpaid internships, and portfolios that resemble a seasoned professional, not a fresh graduate. A bachelor’s degree, once the key to entry, is now just the price of admission. Overqualified candidates compete for underpaid jobs, often just to survive.
One Harvard MBA described applying to 1,000 jobs with no results. Companies, inundated by applications, are now so selective that only those who precisely “game the system” have a shot. This has fundamentally flipped the hiring pyramid: enormous demand for experience, shrinking chances for new entrants, and a brutal gauntlet for anyone not perfectly groomed by internships and coaching.
Burnout Before Day One
The cost is more than financial—mental health and optimism are collapsing among the newest generation of workers. Many come out of elite programs and immediately end up in jobs that don’t require degrees, or take positions far below their qualifications just to pay the bills. There’s a sense of burnout before careers even begin, trapping talent in a cycle of exhaustion, frustration, and disillusionment.
Cultural Collapse: From Relationships to Algorithms
What’s really broken? The culture of hiring itself. Companies have traded trust, mentorship, and relationships for metrics, optimizations, and cost-cutting. Managers no longer hire on potential—they rely on machines, rankings, and personality tests that filter out individuality and reward those who play the algorithmic game best.
AI has automated the very entry-level work that used to build careers—research, drafting, and analysis—and erased the first rung of the professional ladder for thousands of new graduates. The result is a workforce filled with people who know how to pass tests, not necessarily solve problems or drive innovation.
The Ghost Job Phenomenon
Up to half of all listings for entry-level jobs may be “ghost jobs”—positions posted online for optics, compliance, or future needs, but never intended for real hiring. This means millions of job seekers spend hours on applications destined for digital purgatory, further fueling exhaustion and cynicism.
Not Lazy—Just Locked Out
Despite the headlines, the new class of unemployed graduates is not lazy or entitled—they are overqualified, underleveraged, and battered by a broken process. Harvard’s brand means less to AI and ATS systems than the right keyword or résumé format. Human judgment has been sidelined; individuality is filtered out.

What’s Next? Back to Human Connection
Unless companies rediscover the value of human potential, mentorship, and relationships, the job search will remain a brutal numbers game—one that even the “best and brightest” struggle to win. The current system doesn’t just hurt workers—it holds companies back from hiring bold, creative talent who don’t fit perfect digital boxes.
Key Facts:
- 25% of Harvard MBAs unemployed, highest on record
- Only 30% of 2025 grads nationwide have jobs in their field
- Nearly half of grads feel unprepared for real work
- Up to 50% of entry-level listings are “ghost jobs”
- AI and ATS have replaced human judgment at most companies
If you’ve felt this struggle—or see it happening around you—share your story in the comments. And make sure to subscribe for more deep dives on the reality of today’s economy and job market.
This is not just a Harvard problem. It’s a sign that America’s job engine is running on empty, and it’s time to reboot—before another generation is locked out.

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoWicked Sequel Disappoints Fans: Audience Verdict on For Good

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoAriana & Cynthia Say They’re in a ‘Non‑Demi Curious, Semi‑Binary’ Relationship… WTF Does That Even Mean?

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMexico Bans Dophin Shows Nationwide

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoColombia’s ‘Doll’ Arrest: Police Say a 23-Year-Old Orchestrated Hits, Including Her Ex’s Murder

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoHow The Grinch Became The Richest Christmas Movie Ever

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoMiley Cyrus Is Engaged to Maxx Morando

 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks agoLuana Lopes Lara: How a 29‑Year‑Old Became the Youngest Self‑Made Woman Billionaire

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoUS May Completely Cut Income Tax Due to Tariff Revenue