World News
Cyber insurance audit: Painful necessity, or a valuable opportunity? on July 28, 2023 at 12:00 pm
Not that long ago, few companies even considered purchasing insurance to mitigate their financial exposure from a cyber incident, and for those that did, obtaining a policy was as easy as filling out an application and writing a check. Those days are now squarely in the rearview mirror. Today, companies everywhere are rushing to get cyber insurance — the value of the global cyber insurance market reached $13.33 billion in 2022 and is projected to soar to $84.62 billion by 2030.
However, the increased number of policies combined with the sharp uptick in costly attacks led to higher costs for cybersecurity insurance providers. To stem their losses, insurance companies now often require proof that an organization has implemented a variety of security measures in order to be eligible to purchase a policy.
Rather than resisting or resenting risk assessments from potential cyber insurance vendors, IT leaders should regard them as an opportunity to strengthen their organization’s security posture.
Cyber insurance involves risk assessment
Across the insurance industry, policy requirements and premiums vary according to risk assessment. For instance, installing an anti-theft system might reduce the cost of insuring an expensive sports car. A person living in a flood plain can expect to pay more for a homeowner’s policy than someone with a similar house on higher ground — or they might not be able to purchase a policy at all, as homeowners in states like Florida are discovering.
It is the same for cyber insurance. An insurance provider may impose more security demands on a company that hosts large volumes of personally identifiable information (PII) than it does for a company of similar size with far less PII. And organizations that lack sufficient security controls to bring risk down to a level acceptable to an insurance provider might not be eligible for any policy at any price.
What cyber insurance actually covers
The main focus of cyber insurance is obviously on covering the financial risks of an incident. Typically, you can expect the insurance to cover the firsthand costs to the business that are the direct result of the cyber event, such as:
Forensic analysis and incident response. Some insurers require that you engage specific managed incident response services.
Recovery of data and systems caused by actual loss and destruction.
Cost of the downtime due to the cyber event.
Costs incurred from sensitive data breaches, such as handling PR activities, notifying impacted clients, or even providing credit monitoring services to customers.
Legal services and certain types of liability for regulated data, including covering the costs of the civil lawsuits.
It is important to note that insurance rarely or never covers some of the longer-lasting impacts of the event, such as any future profit loss due to theft of intellectual property or the need to invest in cybersecurity program improvements after the event.
There is no consensus on reimbursement for paying a ransom. Not all insurers cover this type of expense. Some experts argue that it can encourage further attacks and fund criminal activities. In some jurisdictions, the discussion is going back and forth on whether paying ransom should be banned altogether.
As with any insurance policy, you can expect extra clauses. These may include the top amount they cover, the requirement to go through a due process with the law enforcement agencies, or involvement in professional ransom-negotiation services.
The must-have security measures for cyber insurance
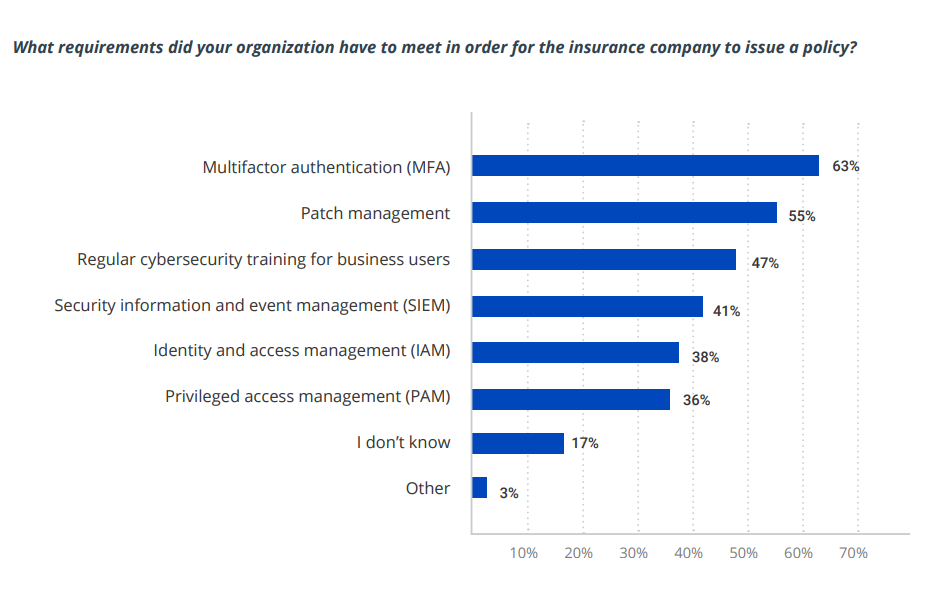
A recent Netwrix study reveals useful details about the process of qualifying for cyber insurance today. It found that 50% of organizations with cyber insurance implemented additional security measures either to meet the requirements of the policy they selected or to simply be eligible for a policy at all. The figure below shows the specific requirements they reported having to meet:
Image Credits: Netwrix/Netwrix Hybrid Trends Security Report 2023
Don’t take this list as comprehensive or authoritative. For instance, implementing MFA does not necessarily mean requiring MFA for all users; an insurer might require additional authentication only for users with privileged access to sensitive data and systems. In addition, remember that these controls are interrelated. For example, in order to require MFA for access to particular types of data, you need to know where sensitive and regulated data resides and have control over user and administrative privileges.
The value of the global cyber insurance market reached $13.33 billion in 2022 and is projected to soar to $84.62 billion by 2030.
News
US May Completely Cut Income Tax Due to Tariff Revenue

President Donald Trump says the United States might one day get rid of federal income tax because of money the government collects from tariffs on imported goods. Tariffs are extra taxes the U.S. puts on products that come from other countries.

What Trump Is Saying
Trump has said that tariff money could become so large that it might allow the government to cut income taxes “almost completely.” He has also talked about possibly phasing out income tax over the next few years if tariff money keeps going up.
How Taxes Work Now
Right now, the federal government gets much more money from income taxes than from tariffs. Income taxes bring in trillions of dollars each year, while tariffs bring in only a small part of that total. Because of this gap, experts say tariffs would need to grow by many times to replace income tax money.
Questions From Experts
Many economists and tax experts doubt that tariffs alone could pay for the whole federal budget. They warn that very high tariffs could make many imported goods more expensive for shoppers in the United States. This could hit lower- and middle‑income families hardest, because they spend a big share of their money on everyday items.
What Congress Must Do
The president can change some tariffs, but only Congress can change or end the federal income tax. That means any real plan to remove income tax would need new laws passed by both the House of Representatives and the Senate. So far, there is no detailed law or full budget plan on this idea.

What It Means Right Now
For now, Trump’s comments are a proposal, not a change in the law. People and businesses still have to pay federal income tax under the current rules. The debate over using tariffs instead of income taxes is likely to continue among lawmakers, experts, and voters.
News
Epstein Files to Be Declassified After Trump Order

Former President Donald Trump has signed an executive order directing federal agencies to declassify all government files related to Jeffrey Epstein, the disgraced financier whose death in 2019 continues to fuel controversy and speculation.
The order, signed Wednesday at Trump’s Mar-a-Lago estate, instructs the FBI, Department of Justice, and intelligence agencies to release documents detailing Epstein’s network, finances, and alleged connections to high-profile figures. Trump described the move as “a step toward transparency and public trust,” promising that no names would be shielded from scrutiny.
“This information belongs to the American people,” Trump said in a televised statement. “For too long, powerful interests have tried to bury the truth. That ends now.”
U.S. intelligence officials confirmed that preparations for the release are already underway. According to sources familiar with the process, the first batch of documents is expected to be made public within the next 30 days, with additional releases scheduled over several months.
Reactions poured in across the political spectrum. Supporters praised the decision as a bold act of accountability, while critics alleged it was politically motivated, timed to draw attention during a volatile election season. Civil rights advocates, meanwhile, emphasized caution, warning that some records could expose private victims or ongoing legal matters.
The Epstein case, which implicated figures in politics, business, and entertainment, remains one of the most talked-about scandals of the past decade. Epstein’s connections to influential individuals—including politicians, royals, and executives—have long sparked speculation about the extent of his operations and who may have been involved.

Former federal prosecutor Lauren Fields said the release could mark a turning point in public discourse surrounding government transparency. “Regardless of political stance, this declassification has the potential to reshape how Americans view power and accountability,” Fields noted.
Officials say redactions may still occur to protect sensitive intelligence or personal information, but the intent is a near-complete disclosure. For years, critics of the government’s handling of Epstein’s case have accused agencies of concealing evidence or shielding elites from exposure. Trump’s order promises to change that narrative.
As anticipation builds, journalists, legal analysts, and online commentators are preparing for what could be one of the most consequential information releases in recent history.
Politics
Netanyahu’s UN Speech Triggers Diplomatic Walkouts and Mass Protests
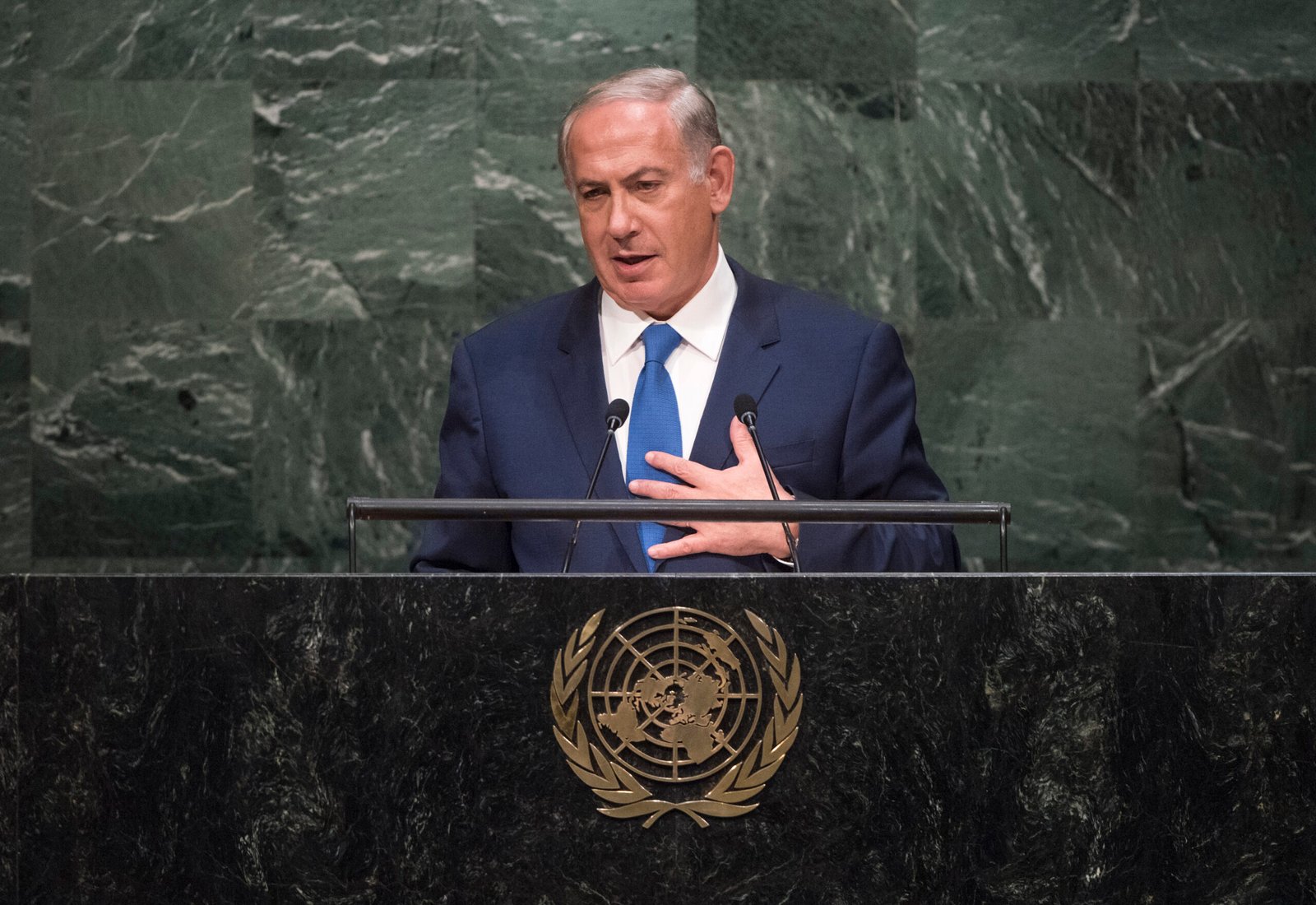

What Happened at the United Nations
On Friday, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu addressed the United Nations General Assembly in New York City, defending Israel’s ongoing military operations in Gaza. As he spoke, more than 100 delegates from over 50 countries stood up and left the chamber—a rare and significant diplomatic walkout. Outside the UN, thousands of protesters gathered to voice opposition to Netanyahu’s policies and call for accountability, including some who labeled him a war criminal. The protest included activists from Palestinian and Jewish groups, along with international allies.

Why Did Delegates and Protesters Walk Out?
The walkouts and protests were a response to Israel’s continued offensive in Gaza, which has resulted in widespread destruction and a significant humanitarian crisis. Many countries and individuals have accused Israel of excessive use of force, and some international prosecutors have suggested Netanyahu should face investigation by the International Criminal Court for war crimes, including claims that starvation was used as a weapon against civilians. At the same time, a record number of nations—over 150—recently recognized the State of Palestine, leaving the United States as the only permanent UN Security Council member not to join them.
International Reaction and Significance
The diplomatic walkouts and street protests demonstrate increasing global concern over the situation in Gaza and growing support for Palestinian statehood. Several world leaders, including Colombia’s President Gustavo Petro, showed visible solidarity with protesters. Petro called for international intervention and, controversially, for US troops not to follow orders he viewed as supporting ongoing conflict. The US later revoked Petro’s visa over his role in the protests, which he argued was evidence of a declining respect for international law.

Why Is This News Important?
The Gaza conflict is one of the world’s most contentious and closely-watched issues. It has drawn strong feelings and differing opinions from governments, activists, and ordinary people worldwide. The United Nations, as an international organization focused on peace and human rights, is a key arena for these debates. The events surrounding Netanyahu’s speech show that many nations and voices are urging new action—from recognition of Palestinian rights to calls for sanctions against Israel—while discussion and disagreement over the best path forward continue.
This episode at the UN highlights how international diplomacy, public protests, and official policy are all intersecting in real time as the search for solutions to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains urgent and unresolved.

 Film Industry2 weeks ago
Film Industry2 weeks agoTurning One Short Film into 12 Months of Content

 Film Industry3 weeks ago
Film Industry3 weeks ago10 Ways Filmmakers Are Building Careers Without Waiting for Distributors

 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days agoWhat the Epstein Files Actually Say About Jay-Z

 Film Industry1 week ago
Film Industry1 week agoAI Didn’t Steal Your Job. It Revealed Who Actually Does the Work.

 Film Industry2 weeks ago
Film Industry2 weeks agoHow to Write a Logline That Makes Programmers Hit Play

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCatherine O’Hara: The Comedy Genius Who Taught Us That Character Is Everything

 Entertainment5 days ago
Entertainment5 days agoYou wanted to make movies, not decode Epstein. Too late.

 Entertainment15 hours ago
Entertainment15 hours agoWhat Epstein’s Guest Lists Mean for Working Filmmakers: Who Do You Stand Next To?



























